黄芪(Astragalus membranaceus)是一种著名的传统药用植物。然而,干旱和镉(Cd)污染是影响植物生长和产量的主要非生物胁迫因素。利用有益的内生真菌可提高宿主植物的抗逆能力。
为了评估深色有隔内生真菌(dark septate endophytes,DSE)对各种非生物胁迫的耐受性,贺学礼团队采用固体平板培养基和液体摇床培养相结合的方式,对不同干旱和镉胁迫条件下10株DSE[Microsphaeropsis cytisi(Mc),Alternaria alstroemeriae(Aa),Stagonosporopsis lupini(Sl),Neocamarosporium phragmitis(Np),Paraphoma chlamydocopiosa(Pc),Macrophomina phaseolina(Mp’),Papulaspora equi(Pe),Alternaria tellustris(At),Macrophomina pseudophaseolina(Mp), andParaphoma radicina(Pr)]进行了体外研究。试验包括使用不同浓度的PEG (0、9、18和27%)和Cd2+(0、25、50和100 mg/L)模拟对DSE的不同胁迫条件。此外,还研究了不同田间持水量(70%和40%)和不同CdCl2浓度(0、5、10和15 mg Cd/kg)下DSE (Np和At)对黄芪生长的影响。
Groups |
Treatment Group |
Methods |
Control group |
CK |
70% field water capacity |
Cd stress group |
Cd1 |
5 mg Cd/kg soil |
Cd2 |
10 mg Cd/kg soil |
Cd3 |
15 mg Cd/kg soil |
Drought stress group |
D |
40% field water capacity |
Drought-Cd interaction stress group |
DCd1 |
40% field water capacity and 5 mg Cd/kg soil |
DCd2 |
40% field water capacity and 10 mg Cd/kg soil |
DCd3 |
40% field water capacity and 15 mg Cd/kg soil |
Inoculation group |
Np |
Inoculation with N. phragmitis |
At |
Inoculation with A. tellustris |
Non-inoculation group |
C |
No DSE inoculation |
结果表明,在PEG浓度为18%时,Aa、Np、Pc、Mp′和Mp的菌落生长速率优先达到培养皿最大直径;Aa、Np和At在100 mg Cd/L下仍保持生长活性。另外,选择Aa、Np和At进行干旱和Cd协同胁迫试验。干旱与Cd协同胁迫固体培养结果表明,Np的生长速度明显优于其他菌株。在液体培养条件下,Np和Aa在18% + 25 mg Cd/L浓度下的生物量最高,分别为1.39 g和1.23 g,At在18% + 50 mg Cd/L浓度下的生物量最高,为1.71 g。Np的CAT和POD活性分别在27% + 50 mg Cd/L和27% + 25 mg Cd/L时达最大值。与对照组相比,分别增加了416.97%和573.12%。Aa、Np和At正影响SOD活性。Aa、Np和At的谷胱甘肽(GSH)含量在不同干旱和Cd协同胁迫下均有所增加。结构方程模型(SEM)分析表明,Aa对生物量有正向影响,对Cd含量有负向影响,而Np和At对Cd含量有正向影响。在40%田间持水量单一胁迫和40%田间持水量和5mg Cd/kg的协同胁迫下,Np和At显著增加黄芪的根重。对于DSE应对复合性胁迫的研究有助于丰富微生物技术协助植物抵抗逆境胁迫的研究体系,并对农业种植体系的建立具有指导意义。
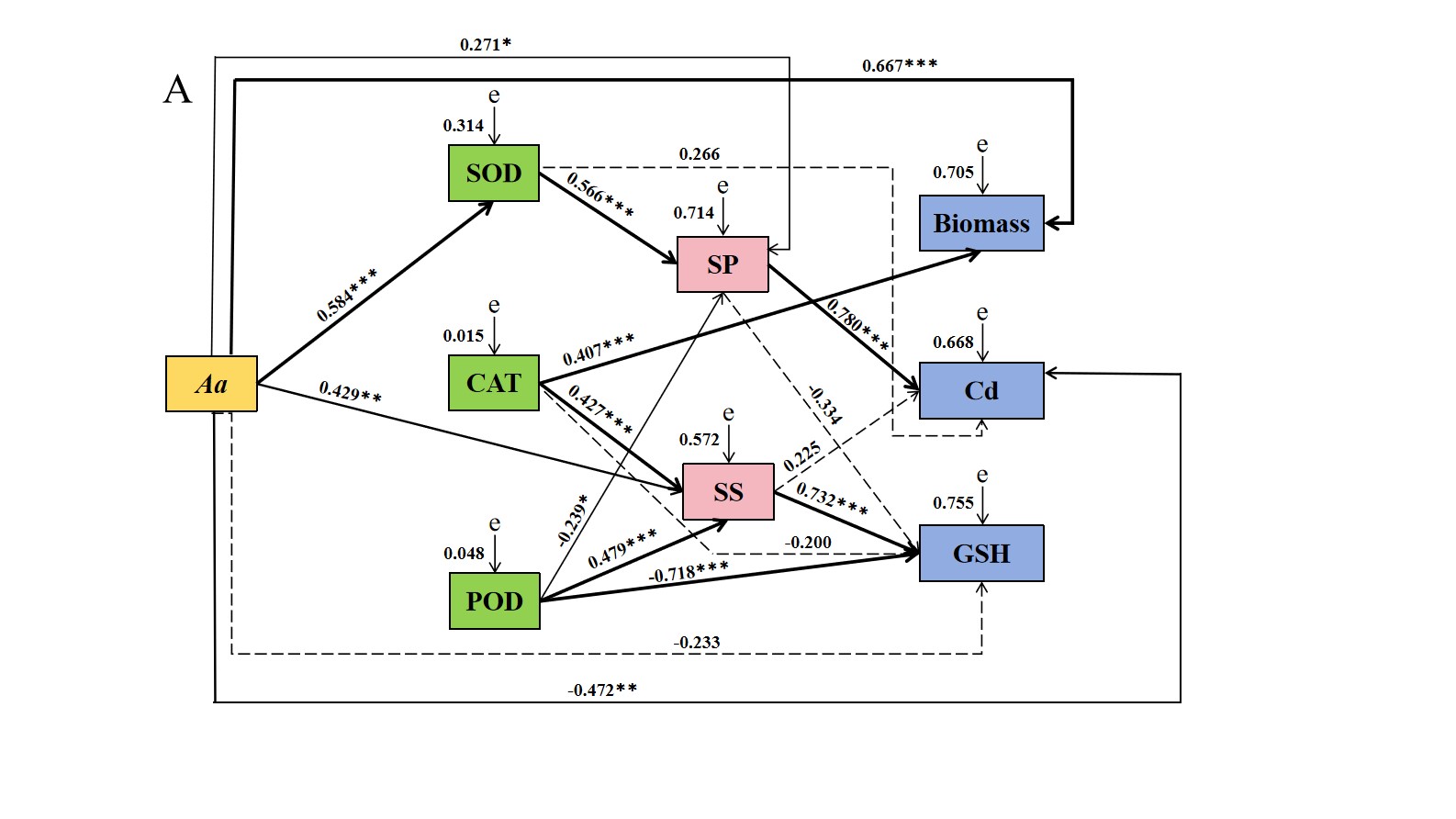
Results of fitness of influencing factors of A. alstroemeriae in structural-equation models
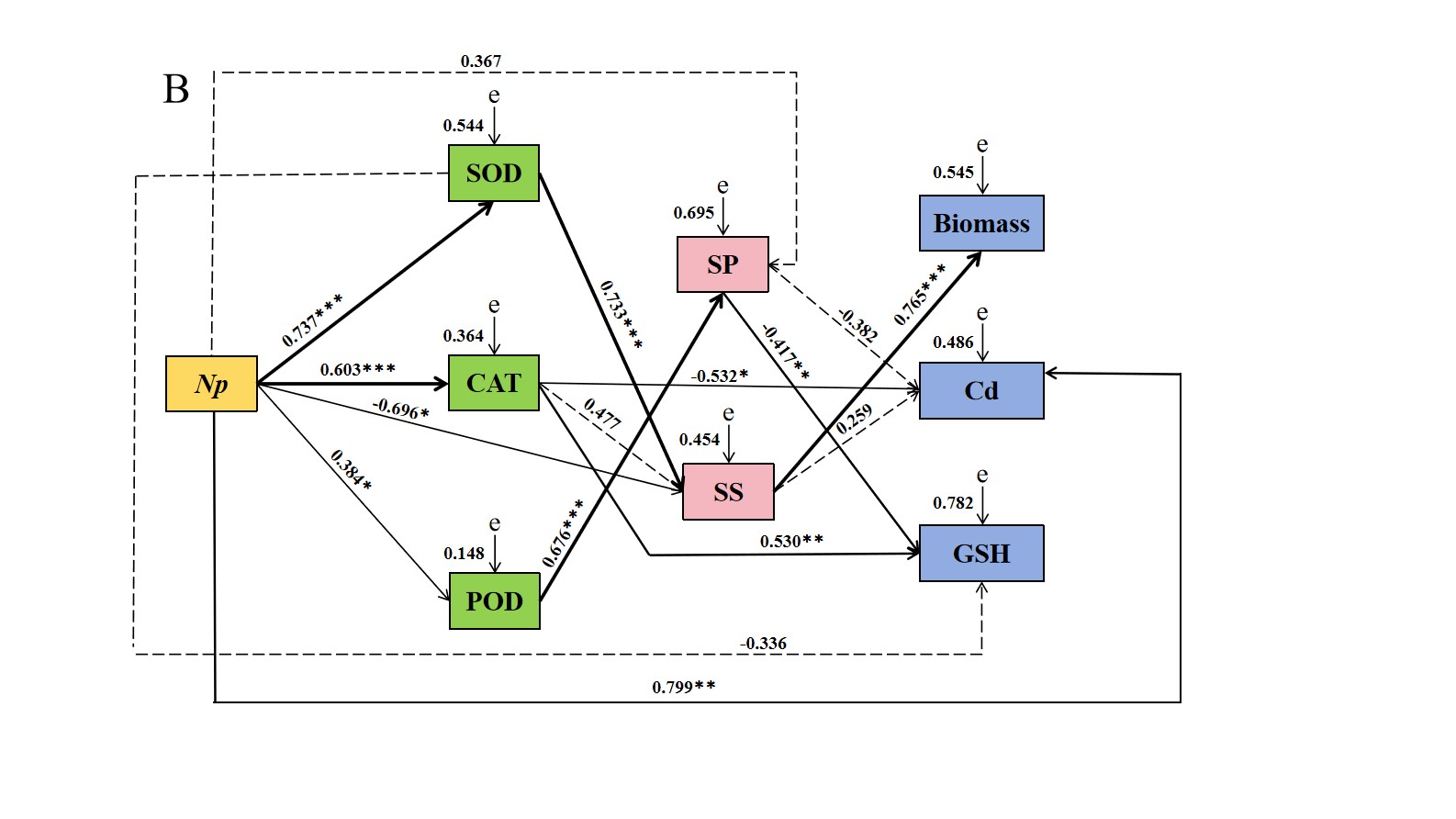
Results of fitness of influencing factors of N. phragmitis in structural-equation models
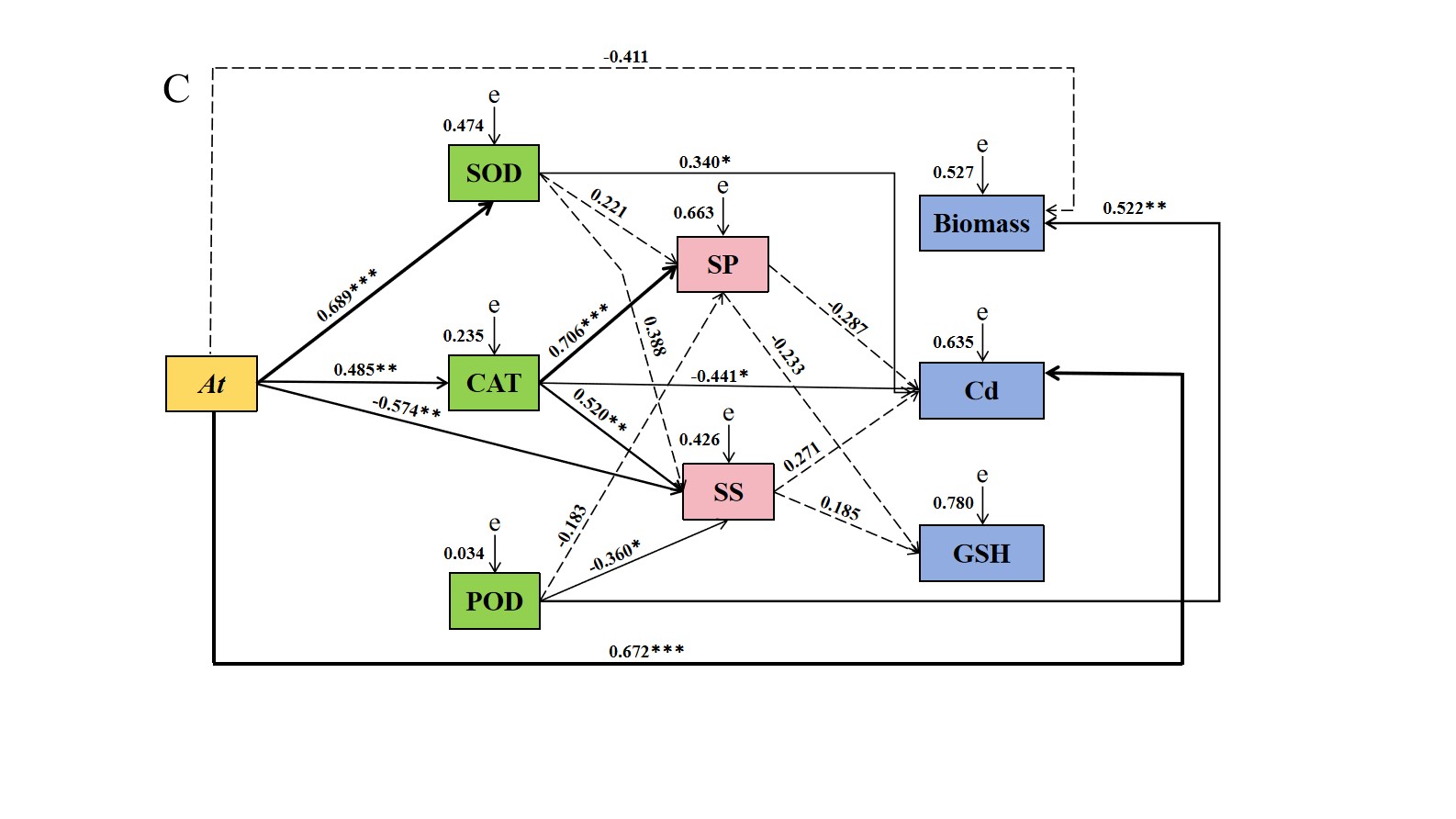
Results of fitness of influencing factors of A. tellustrisin structural-equation models
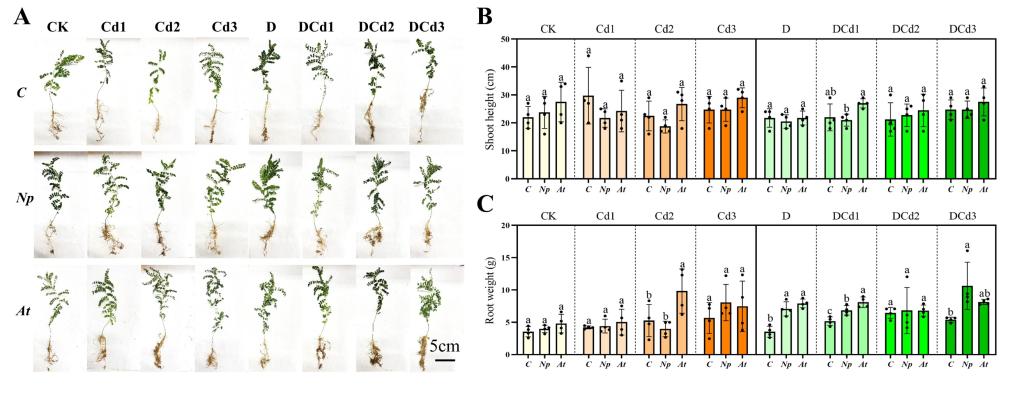
Effect of different DSEs on growth-morphological parameters of Astragalus membranaceus seedlings’ growth under synergistic stress of drought and Cd. Growth picture (A), shoot height (B), and root weight (C) of A. membranaceus under drought and Cd stress. The abbreviations in the figure are non-inoculated plants(C), N. phragmitis (Np), and A. tellustris (At). Means followed by the different letter(s) within each column are significantly different at p < 0.05.
上述成果近日已在期刊Journal of Fungi上发表。河北大学研究生王朵为第一作者,河北大学贺学礼教授和中国医学科学院药用植物研究所贺超副研究员为共同通讯作者,河北大学研究生谢亚丽、张婉怡和姚丽为论文的共同作者。该研究得到了国家重点研发计划项目(2022YFC3501501)、河北省自然科学基金项目(H2022201056)、中央引导地方科技发展资金项目(236Z2904G)的资助。
论文信息:Wang D, Xie Y, Zhang W, Yao L, He C, He X. Study on the Biological Characteristics of Dark Septate Endophytes under Drought and Cadmium Stress and Their Effects on Regulating the Stress Resistance ofAstragalus membranaceus. Journal of Fungi. 2024; 10(7):491.